OutlineParticipation encompasses a series of activities related to
political life, aimed at influencing in a more or less
direct - legal, conventional, pacific or contentious - way
public decisions. Definitions can vary, depending on
whether one focuses on individual or collective actors, on
the social or institutional environment, or on the means
and procedures of participation (Barnes and Kaase
1979).
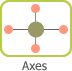
On the horizontal axis, we see the shift from individuals
to collective aggregates as discussed by the sociology
of collective action. A single individual entitled with her
own rights, personal means, resources, and identities
(Milbrath 1965) is opposed to organized aggregates of
people, which can count on organizational resources such
as membership, finances, strategic position in the society
or in the political system, know-how, better access to
information and to channels of expression (Bentley
1908; Olson 1965; Almond and Powell 1966). On the vertical axis, the legislature represents the
institutional arena legitimizing the existence of a democratic
political system and, in turn, legitimized by the
possibility of political participation. Civil society is the
arena where economic and social conflicts are developed and then conveyed to the institutional sphere via various forms of participation.
|